What Kind Of Animals Live In The Savannas Of Africa
Savanna Biome
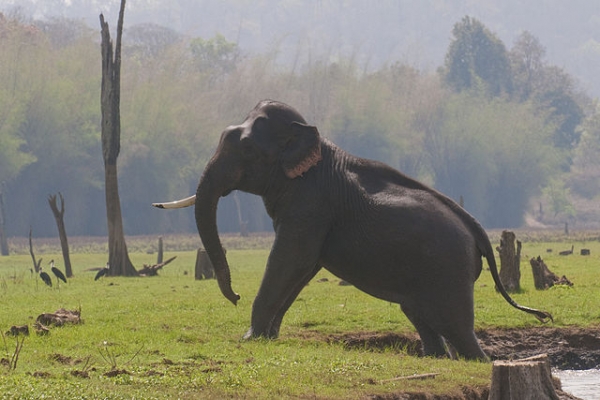
African savanna (jacobeukman, iStockphoto)
African savanna (jacobeukman, iStockphoto)
How does this align with my curriculum?
Learn about the location, plants, animals, human impacts and conservation of the savanna biome.
The Terrestrial Biomes
Theterrestrial world can be divided into areas calledbiomes. A biome is a big surface area of country classified past its distinct plants and animals. The characteristics of each biome are dependent on its temperature and the amount of precipitation the area receives. The plants and animals institute in each biome are adjusted to the particular environment of the biome.
A biome is made up of manyecosystems. An ecosystem is the interaction of living and nonliving things in an environment. Still, a biome is the specific geographic area in which ecosystems tin be constitute.
For the purpose of this backgrounder we will identify major terrestrial biomes of the world based on the Whittaker biome classification scheme. It is interesting to annotation that non anybody agrees on the number and types of biomes.
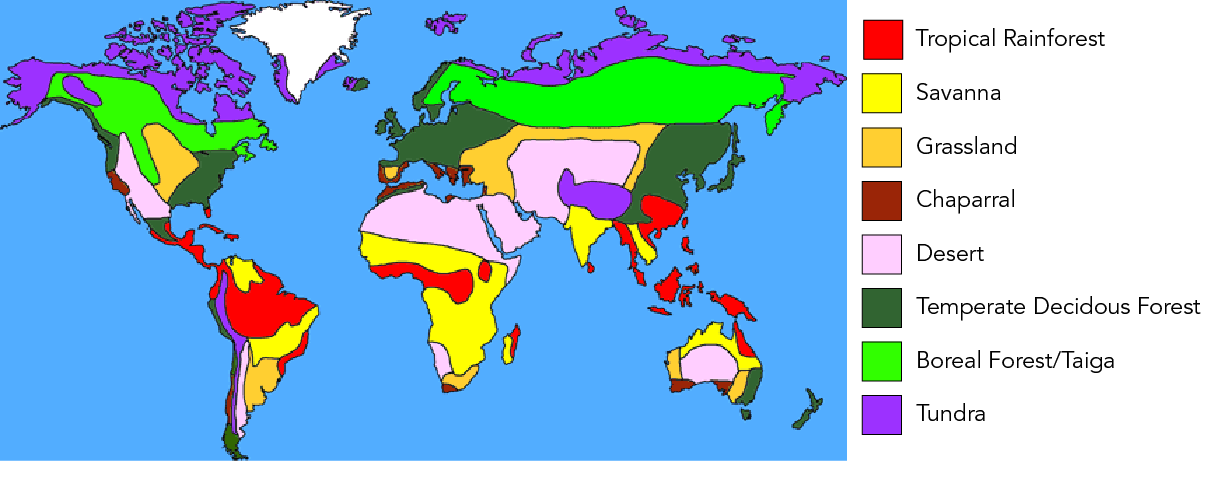
Distribution of the World'southward Major Biomes
The map below shows where each of the viii major terrestrial biomes are located in the world. Canada contains 4 biomes: temperate deciduous wood, grassland, boreal forest/taiga, and tundra. A biome has the same characteristics in any part of the world when it tin be found. Therefore, the boreal forests of Canada await like the boreal forests of Russian federation. The characteristics of each biome are dependent on its climate, peculiarly temperature and the amount of precipitation the expanse receives.
Savannas
Location
Savannas are found all around the world. There are v different types of savannas:
- Tropical and subtropical savannas: found well-nigh the equator and bordered past tropical rainforests and deserts (due east.grand., theSerengeti in Africa)
- Temperate savannas: found in mid-latitude regions (e.g., temperate savanna ofSoutheast Australia)
- Mediterranean savannas: besides found in mid-latitude regions, simply in the Mediterranean (e.grand., theAlentejo region in Portugal)
- Flooded savannas: constitute in thetorrid zone (eastward.one thousand., thePantantal in South America)
- Montane savannas: found in loftier altitude regions (east.g., themountains of Angola in equatorial Africa)
Description
If yous were to climb a tree in the center of a savanna, y'all would encounter kilometres of flat land covered in tall and shortgrasses and spotted withlow-lying shrubs and scattered trees. Savannas are usually atransitional zone between a wood and a grassland. This means that while there are all the same alpine copse, like a forest, they are spread out and the ground is covered in grasses, like a grassland. The climate is also transitional with rotating dry out periods, like a desert, and moisture periods, similar a rainforest. During the winter, no rain falls, and the land is very dry. In the summer, it usually rains quite a lot. This is calledseasonal rainfallbecause it only rains in a certain season.
Plants & Animals
Due to the big amount of grass constitute in savannas, many types ofgrazing mammalscan be establish there. Grazing animals are animals that feed on grasses. These includezebras, wildebeests, elephants, giraffes, ostriches, gazelles, and buffalo.Herds (groups) of grazing animals are usually seen in the African savanna. The savanna biome of sub-Saharan Africa also has the highest variety ofungulates on Earth. Ungulates are hoofed mammals like rhinoceroses, giraffes, camels, hippopotamuses, and elephants.
Manyrodentslive in savannas. Rodents are a mammal group which includes mice and rats. Rodents are often constitute in holes leading to intricate cloak-and-dagger homes calledburrows. In their burrows, the rodents can hide from predators and keep cool.
Savannas are also home to very specialized predatory mammals and birds. The mammals, bothfeline (east.g.,lions andcheetahs) andcanine (due east.g.,African wild dogs), have colouring that allows them to alloy into the grasslands.Raptors (birds of prey), such every bitvultures,eagles andgoshawks, have incredible eyesight, able to spot even a well-camouflaged grassland creature from loftier above.
The constitute-eating animals take developed ways at fugitive predators. Some animals, like the gazelle and ostrich, use speed to endeavour and outrun predators. The giraffe uses its acme to spot predators from far off and the elephant uses its size and strength to go on predators away.
Human Impacts & Conservation
Savannas are field of study to natural wildfires during dry seasons, only humans frequently cause fires besides. Many savanna plants are adapted to thrive afterward fires. Even so, if fires happen too often, it can be damaging to the ecosystem. Savannas are as well often used for farming, which is confusing to the wildlife. This is a big trouble for animals if large farms take over grazing or hunting lands. Developing farmland typically involves clearing trees, which destroys the habitats of animals and other plants that rely on those trees. Farmers likewise allow their domesticated livestock to graze on savannas, which can hateful that there is not enough food for wild animals. This overgrazing can have negative effects on the native plants as well.
For wildlife,poaching is a major threat, specially in Africa. Poaching is the term for hunting animals illegally. Large grazers likeelephants andrhinoceros are hunted for their ivory tusks and horns. This is putting these animals at run a risk. When animals are lost due to poaching, it tin can alter the unabridged ecosystem.
In improver to providing on-the-ground protection for animals, many countries make poaching an criminal offence punishable by prison or heavy fines. All the same, a amend fashion to stop poaching is the ongoing effort to decrease demand for illegal wild animals and wild animals parts. If no ane's buying the products, there will be no need to impale these animals!
As with all biomes, climate change is a huge threat to savannas. As the average global temperature rises due to the emission of greenhouse gases, farthermost weather events, such asdroughts (extremely dry out conditions) have become increasingly astringent. Furthermore, when the landscape is altered by the human being uses described above, savannas are more than likely to flood and burn in an uncontrolled manner.
Sustainable farming methods tin can be put into place to protect the land and wildlife of savannas. This may involve growing more than ane crop on a slice of state so that less infinite is used. Or it may mean growing native species, such as trees, on farmland instead of cutting them downwardly. To keep grazing livestock from competing with wild animals, some farmers feed their animals in stalls rather than letting them graze out on the savanna. There are also ecology organizations and governments that are taking serious action against poaching and illegal wildlife merchandise.
References
Source: https://letstalkscience.ca/educational-resources/backgrounders/savanna-biome
Posted by: grimesmorningard.blogspot.com




0 Response to "What Kind Of Animals Live In The Savannas Of Africa"
Post a Comment